Proximal Humeral Fractures Classification And Treatment Springerlink
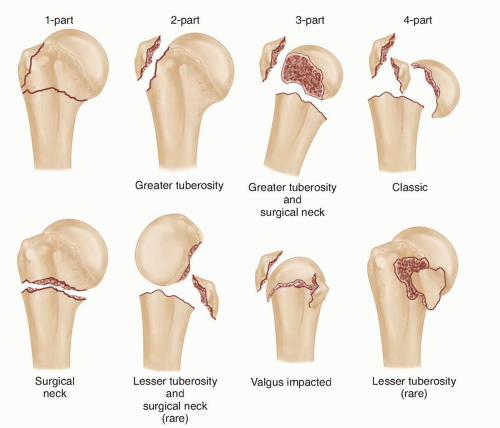
The Neer system divides the proximal humerus into four parts and considers not the fracture line, but the displacement as being significant in terms of classification The four parts are the humeral head, the greater tuberosity, the lesser tuberosity and the humeral shaft Displacement is on a perpart basis Anatomy and Classification of Proximal Humerus Fractures Fig 11 The average humeral neck angle is 130° The superior aspect of the articular surface is 8 mm above the greater tuberosity Average retroversion values are 18–33° The proximal humeral articular surface is a segment of a sphere that measures from 37 to 57 mm in diameter 5
Ao classification proximal humerus fracture
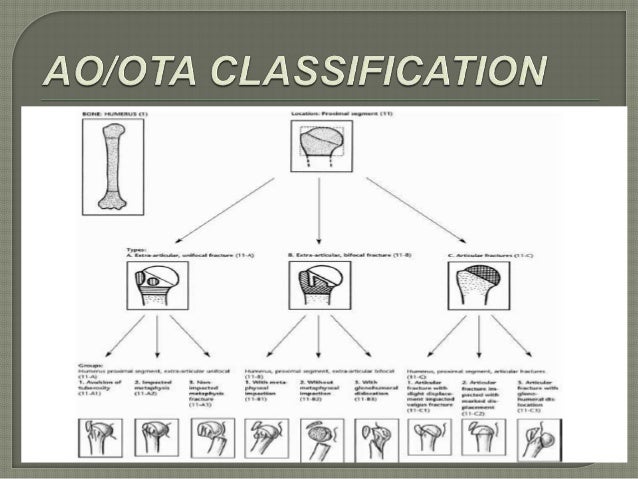
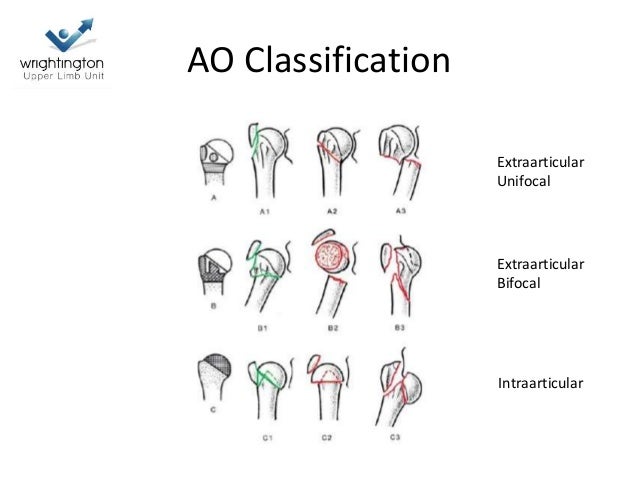
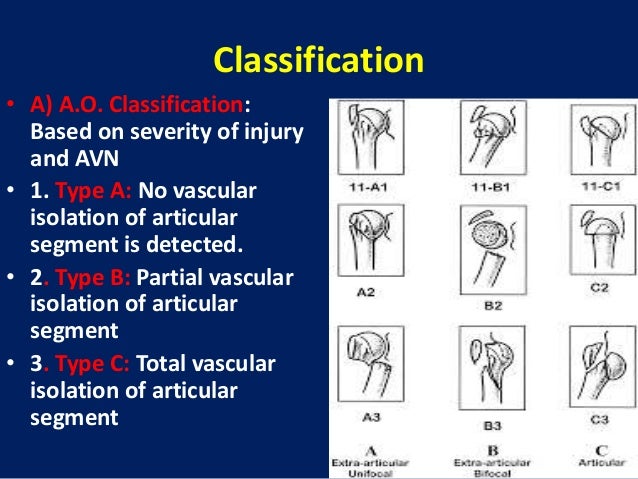
Ao classification proximal humerus fracture- Chapter 62 AO/ASIF Fracture Classification Fig 621 AO/ASIF fracture classification Proximal Humerus Fig 622 AO/ASIF fracture classification proximal humerus Humeral Shaft Fig 623 AO/ASIF fA proximal humerus fracture is a break of the upper part of the bone of the arm () Symptoms include pain, swelling, and a decreased ability to move the shoulder Complications may include axillary nerve or axillary artery injury The cause is generally a fall onto the arm or direct trauma to the arm Risk factors include osteoporosis and diabetes Diagnosis is generally based on Xrays

Pdf Reproducibility Of Three Classifications Of Proximal Humeral Fractures Semantic Scholar
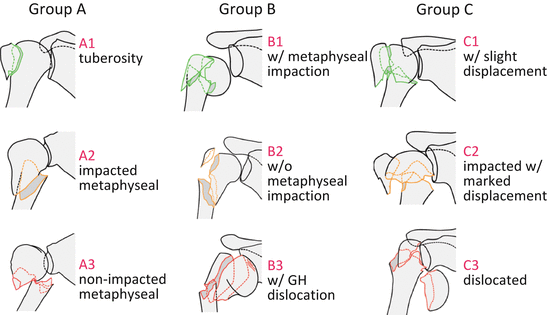
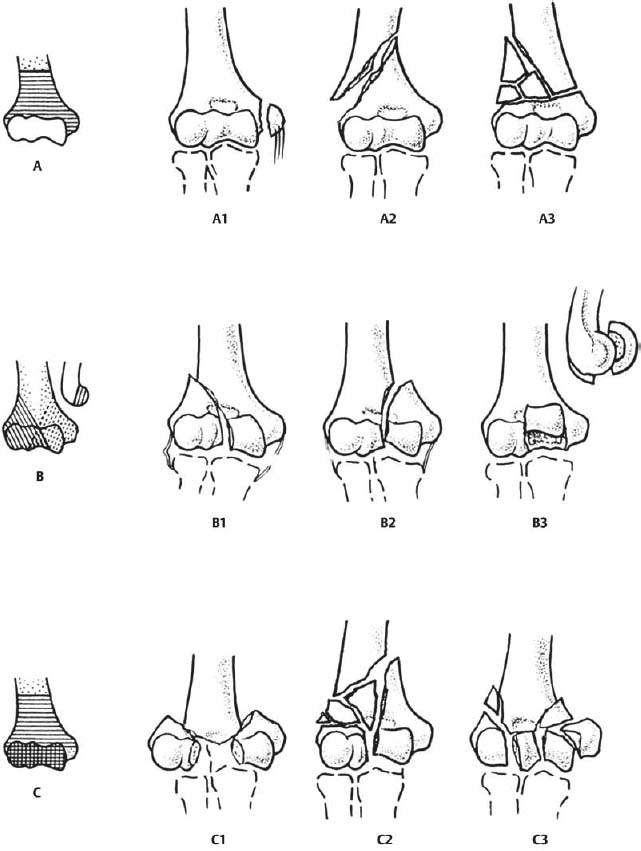
The foursegment classification system defines proximal humerus fractures by the number of displaced segments or parts, with additional categories for articular fractures and dislocations (Fig 1) The potential segments involved are the greater tuberosity, lesser tuberosity, articular surface, and humeral diaphysisFig 5B Noncontact fracture with the shaft displaced medially by the l)ectoualis major and the head held in uieutual rotatiout by the intact rotator cuff Fig 5C Commiuiuted fuactuue, twisted by placing the arm a(ross the chest iii 1 sling DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES lost VOL 52A, NO 6, SEPTEMBER 1970Proximal Humerus Fractures Kevin J Perry, MD DPT Associate Professor • Review the principles of diagnosis and management of proximal humerus fractures • Review fracture classification schemes • Review decision making and treatment options • Review outcomes and evidence Classification • AO/OTA
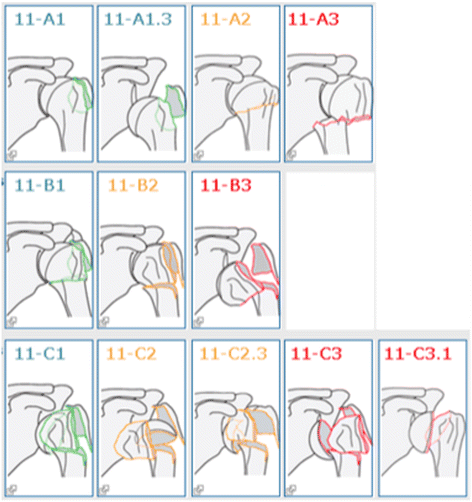
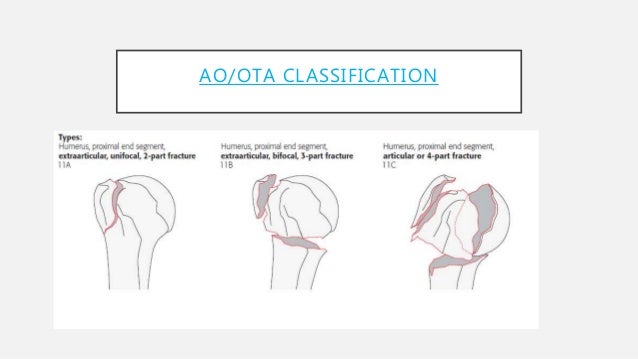
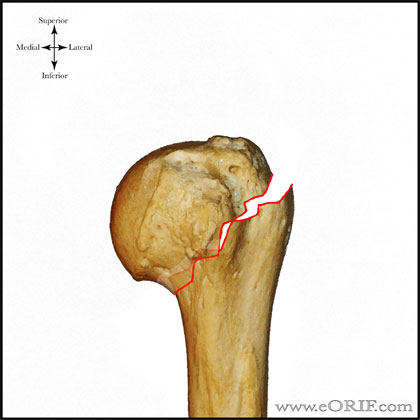
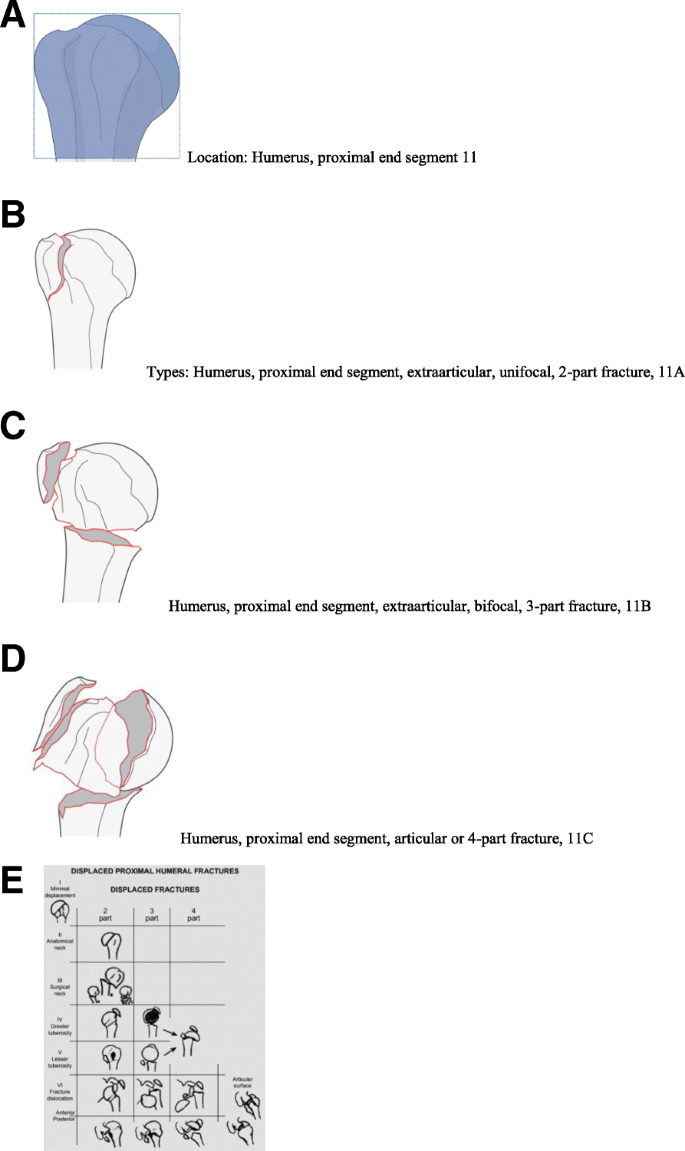
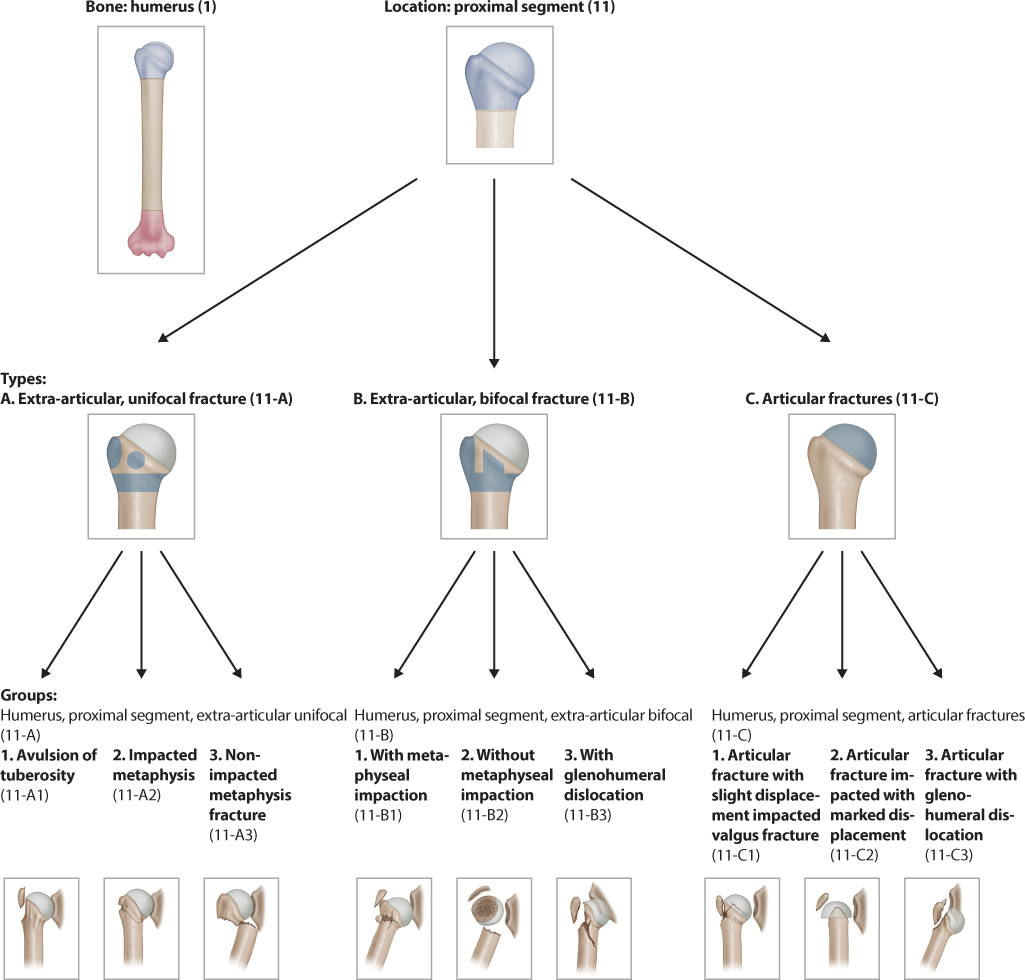
Introduction Several classifications for proximal humeral fractures exist, with excellent reliability and reproducibility of such classifications being a desirable feature Despite their widespread use, these systems are variable in both reliability and accuracy We aimed to, a) assess and compare the reliability of the Neer (complete and abbreviated versions) and Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Overall, the OTA/AO classification system for proximal humeral fractures has nine groups (11A1/2/3, 11B1/2/3, 11C1/2/3) All groups are divided into three subgroups based on the degree of displacement, impaction, or dislocation, resulting in a total of 27 subgroups Papakonstantinou MK, Hart MJ, Farrugins;
Ao classification proximal humerus fractureのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 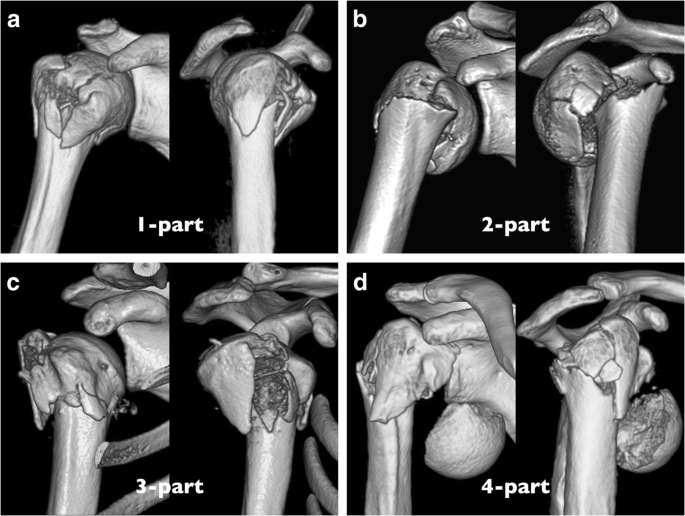 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | 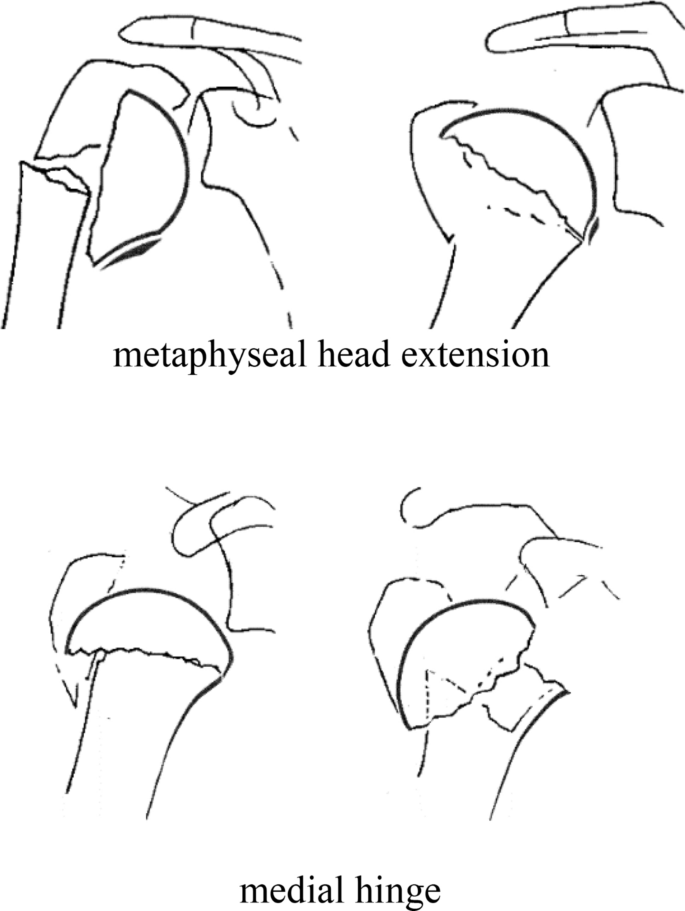 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 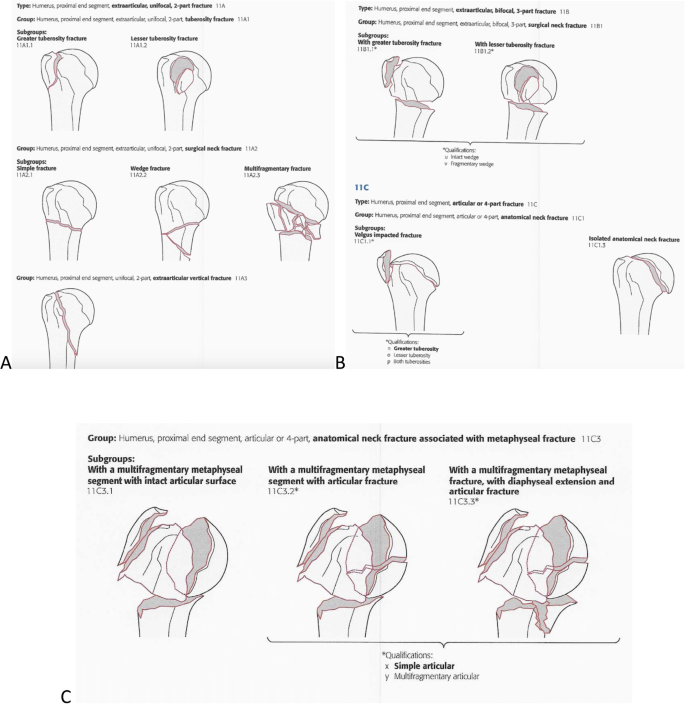 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 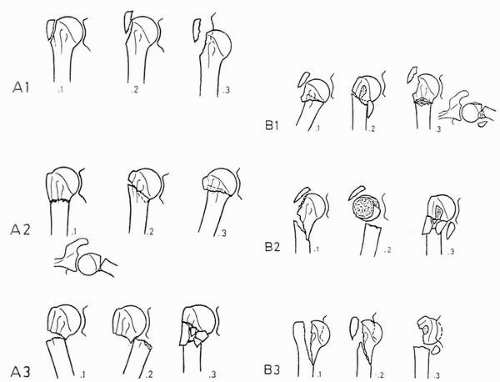 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures | 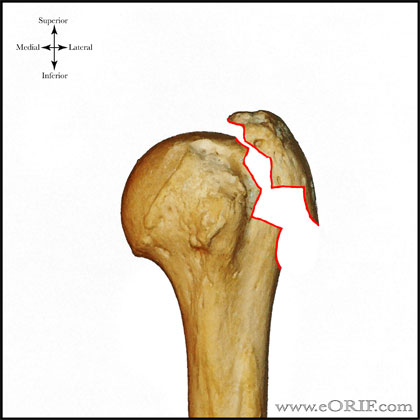 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 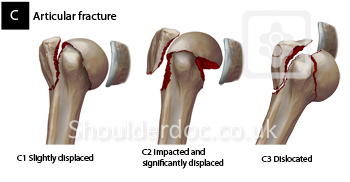 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 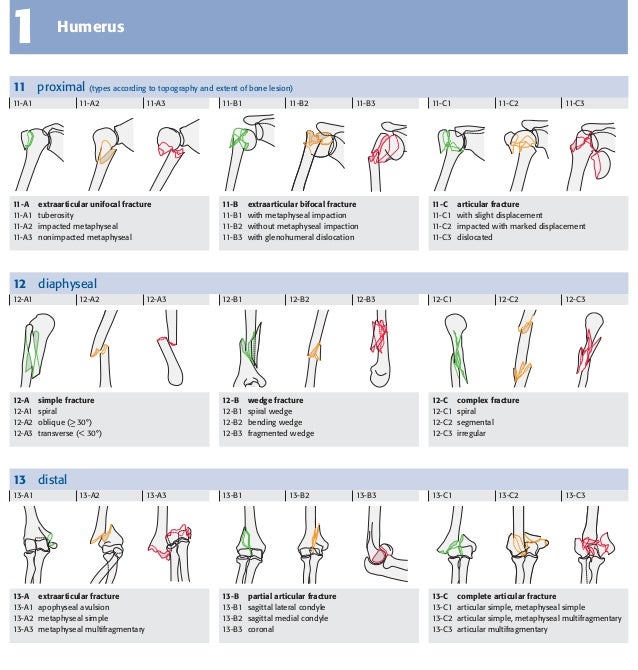 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | 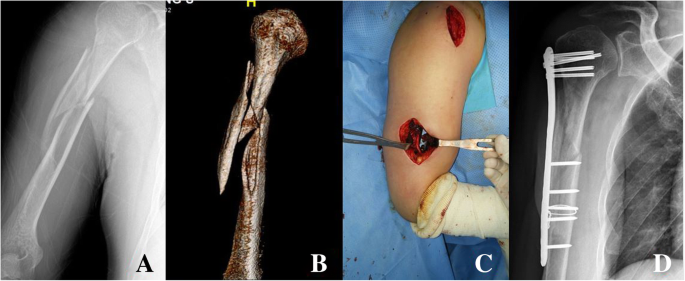 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 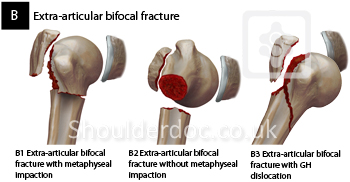 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 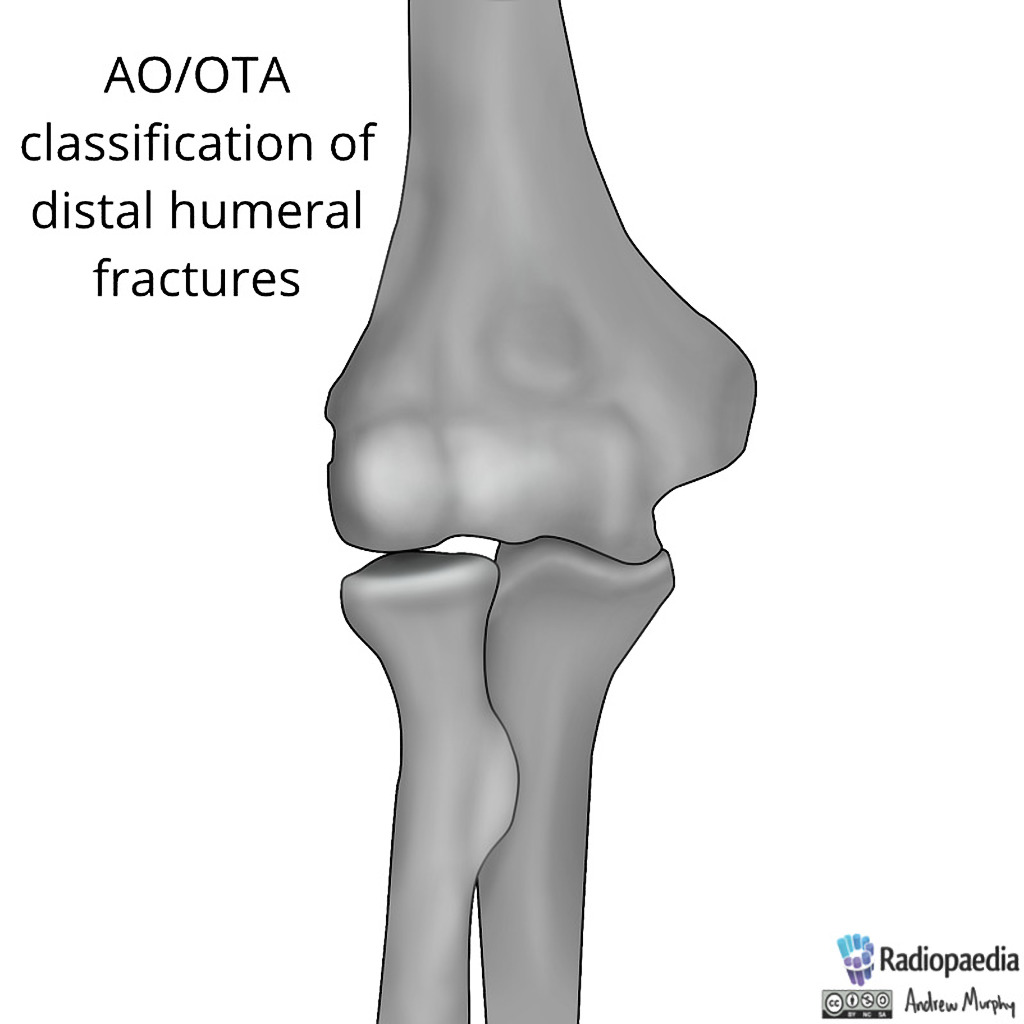 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | 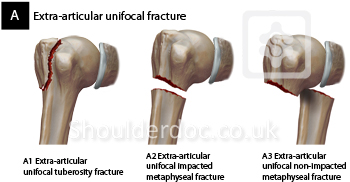 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures | 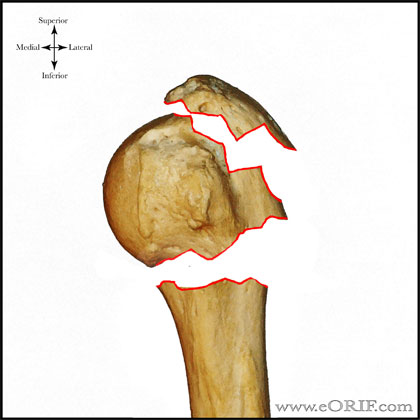 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures | 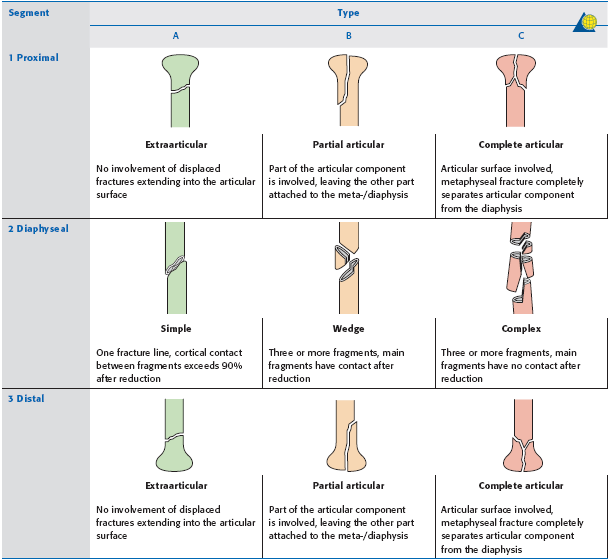 Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | 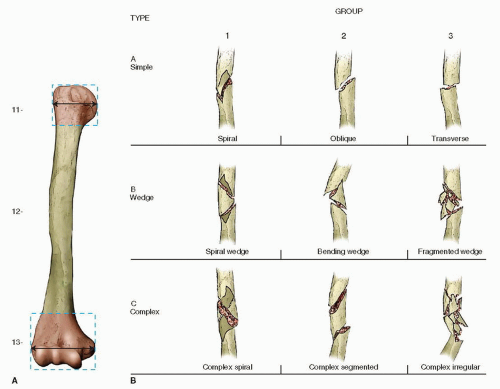 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 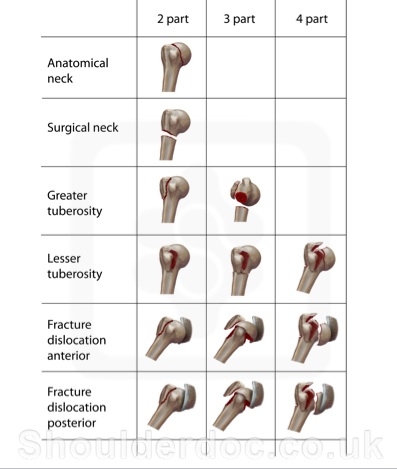 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures | 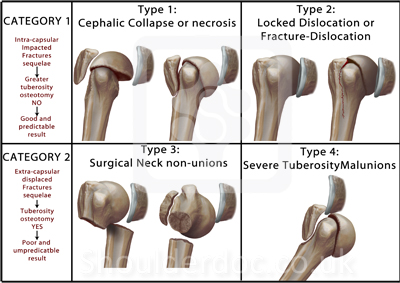 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 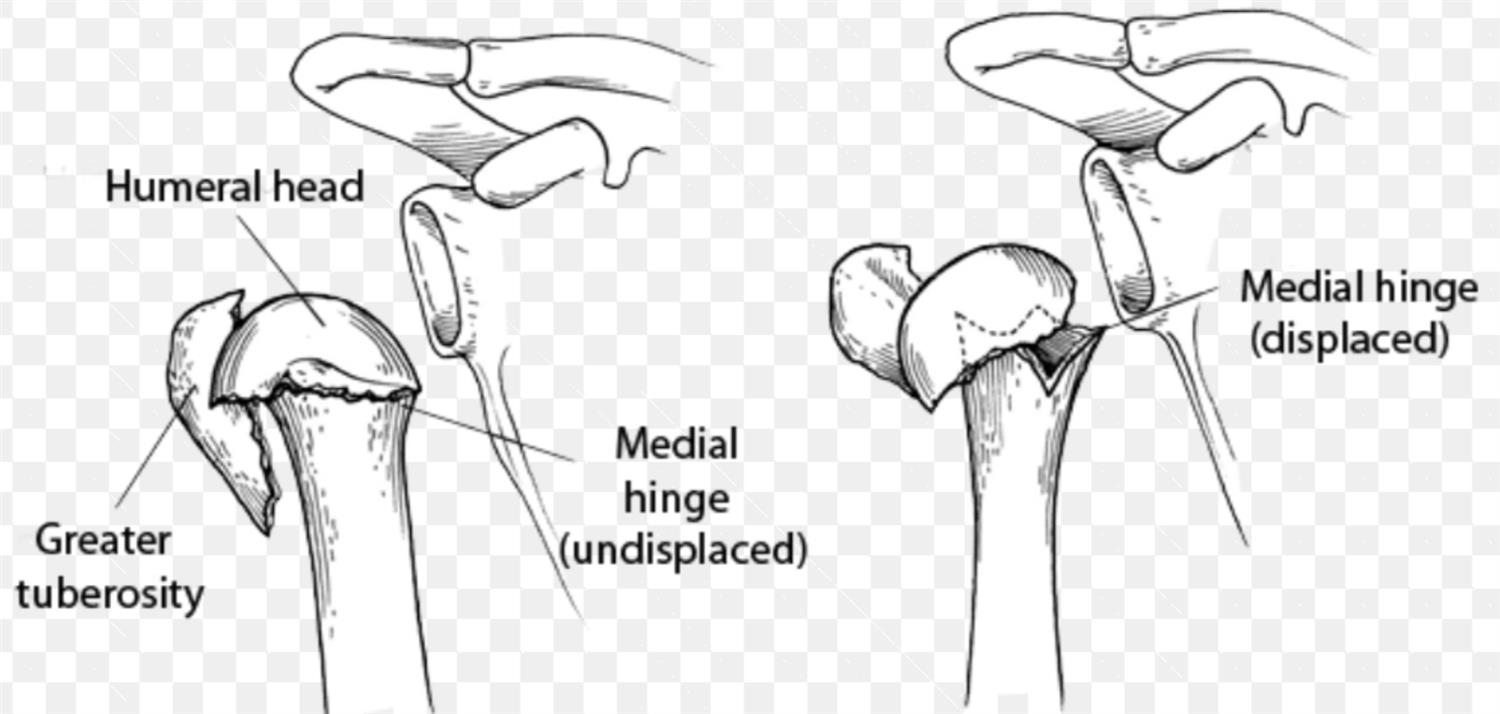 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures | 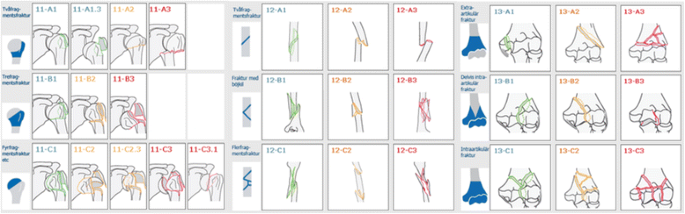 Proximal Humerus Fractures |
 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
「Ao classification proximal humerus fracture」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 Proximal Humerus Fractures | 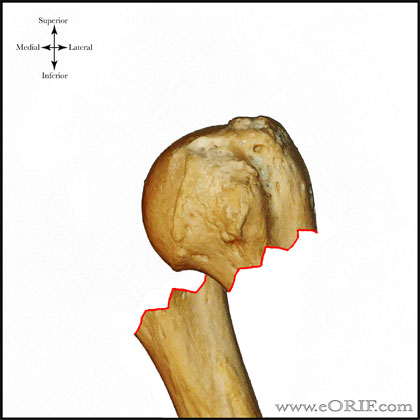 Proximal Humerus Fractures |  Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Proximal Humerus Fractures | Proximal Humerus Fractures |
Type C fractures within the AO/OTA classification Fractures of the proximal humerus are common injuries They comprise about 4% of all fractures3, 4 The incidence is approximately 70 per 100,0005, 6 and it will probably increase due to the association with age and osteoporosis710 Epidemiological research has demonstrated both an overall and an increase of displaced complex proximal humeral fractures that are treated in a clinical setting, affecting especially woman older than 60 years 1–7The Neer and AO/OTA classifications are commonly usedMinimally displaced fractures can successfully be treated nonoperatively 6, 8,
Incoming Term: ao classification proximal humerus fracture,



