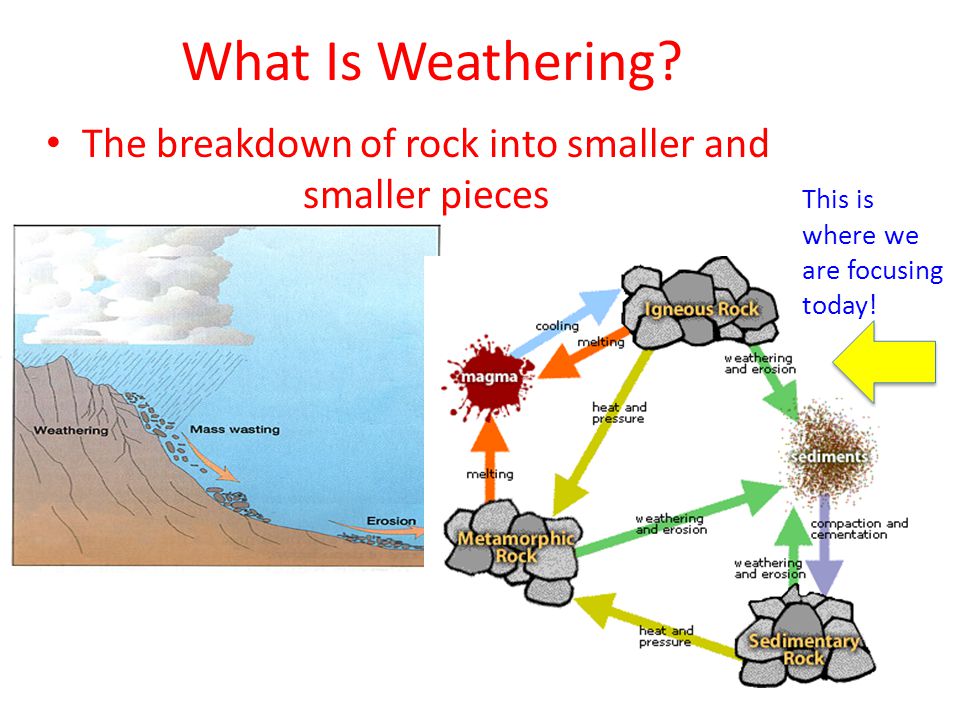
Repetition of this activity results in disintegration of rocks Sometimes rocks disintegrate into small pieces, which is known as Granular disintegration Although main reason for physical weathering is heat of sun yet winds and air pressures can also cause such processPhysical weathering can also refer to other things in the environment breaking down, like soil and mineralsWeathering (breaking down rock) and erosion (transporting rock material) at or near the earth's surface breaks down rocks into small and smaller pieces These smaller pieces of rock (such as sand, silt, or mud) can be deposited as sediments that, after hardening, or lithifying, become sedimentary rocks

Physical Weathering Day One Physical Weathering The Process
How rocks break into pieces in physical weathering
How rocks break into pieces in physical weathering-Weathering is the process that changes solid rock into sediments With weathering, rock is disintegrated into smaller pieces Once these sediments are separated from the rocks, erosion is the process that moves the sediments away from it's original position Water is(physical change) EX plant roots growing (as the roots grow, they break rocks into smaller pieces) EX ice wedging (water fills in the cracks in rocks, then freezes, expands, and breaks the rock) Chemical weathering = when rocks break apart
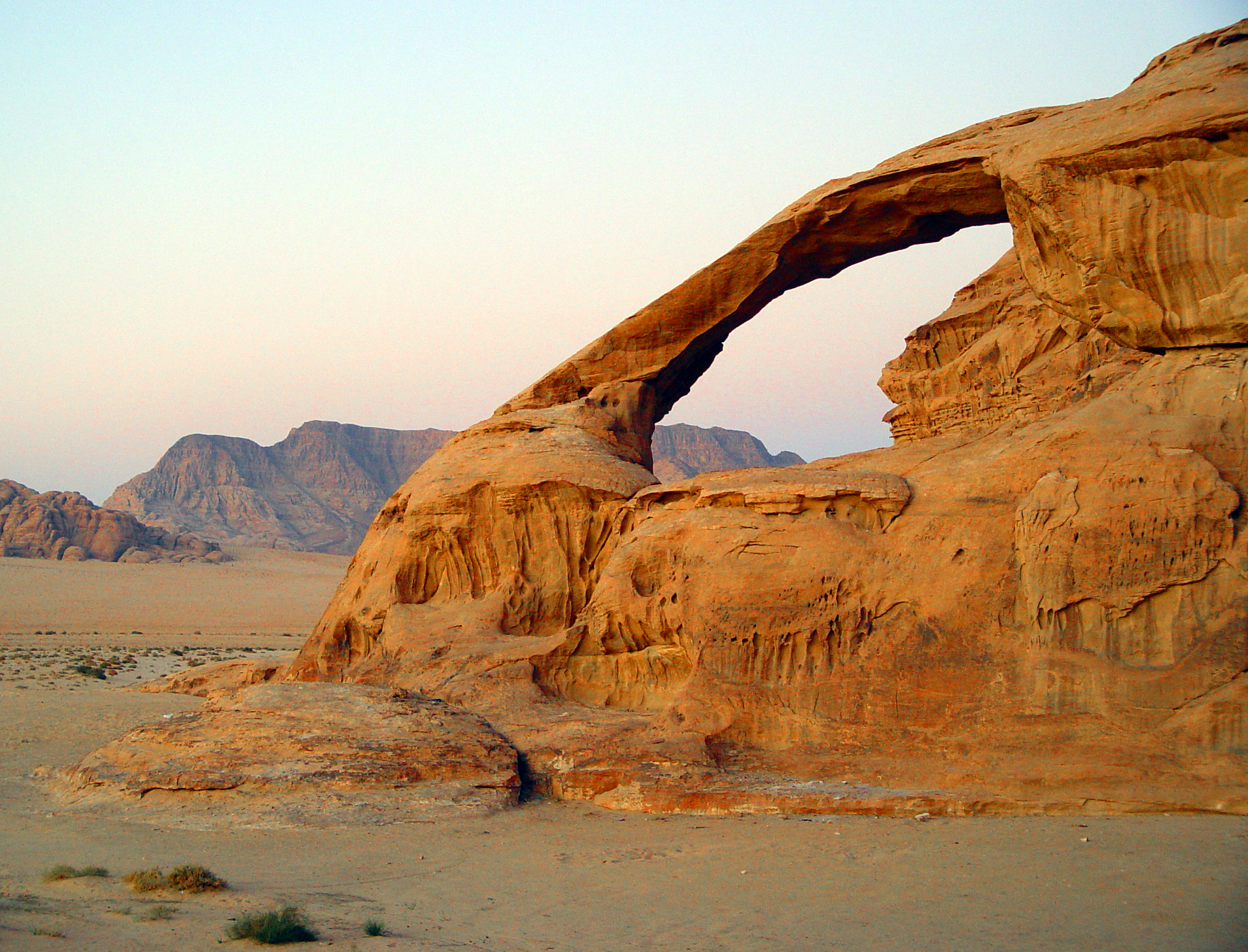




Weathering Wikipedia
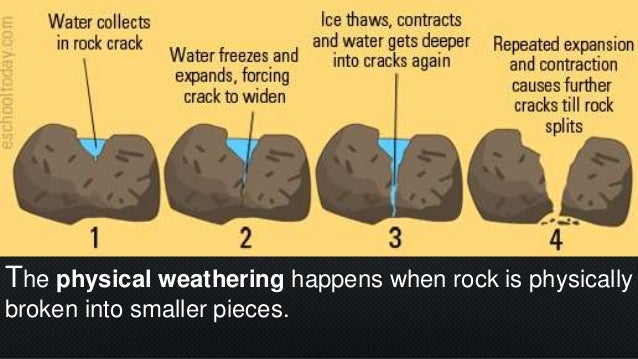
Scientists categorize this processes into two groups physical weathering and chemical weathering Physical weathering (also called mechanical weathering) happens when physical forces repeatedlyIt didn't start out that way!Mechanical weathering physically breaks up rock One example is called frost action or frost shattering Water gets into cracks and joints in bedrock When the water freezes it expands and the cracks are opened a little wider Over time pieces of rock can split off a rock face and big boulders are broken into smaller rocks and gravel
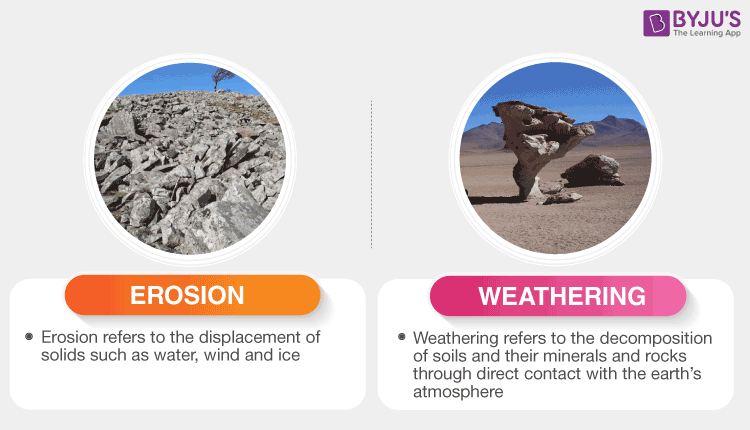
The process of weathering is responsible for erosion If there is no weathering of rocks, erosion will not have any meaning that weathering helps in erosion and shortening of relief The process of weathering divides the rocks into small pieces and provides a route for soil formation Hence weathering is an important process of soil formationWilliam F Bleam, in Soil and Environmental Chemistry, 12 The Jackson Weathering Sequence Physical weathering and abrasion generate finegrained particles that retain the mineralogy of the rocks from which they form sand (diameter range 005– mm) particlesize classSoil is defined as any material that passes a mm sieve Chemical weathering transforms primary (rockMechanical weathering, or physical weathering, is the process by which rocks and minerals break down into smaller pieces without changing their composition Factors affecting Mechanical Weathering 1 Temperature a Water collects in the cracks of rocks and rock layers b In freezing temperatures, water freezes, expands, exerts pressure on the
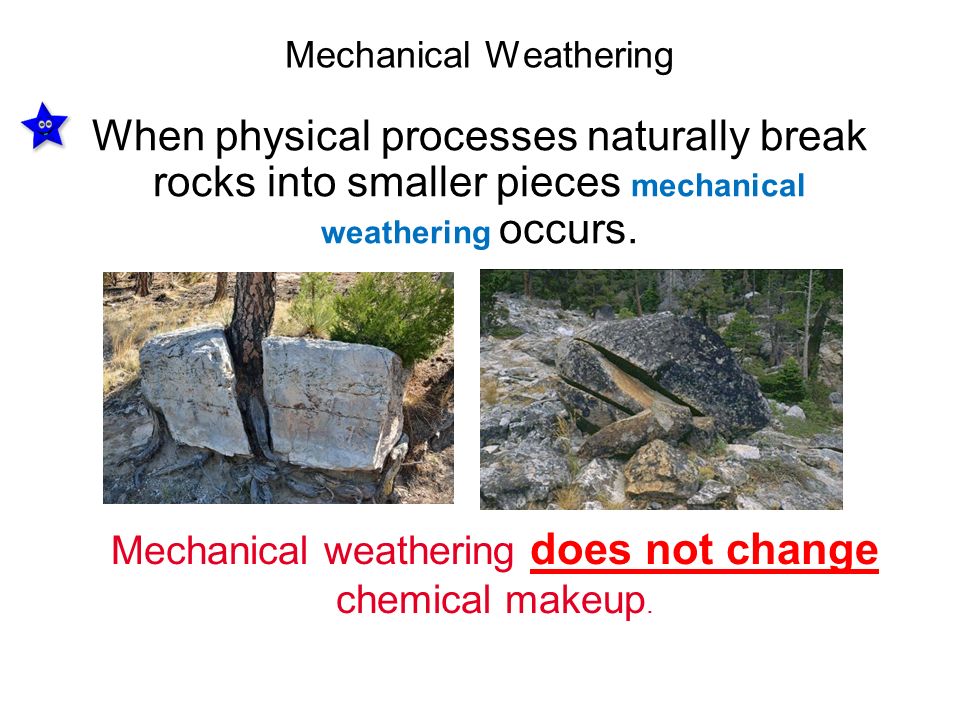
Mechanical weathering happens when rocks are broken into pieces by physical means There are many agents, or causes, of mechanical weathering ICE Ice is one agent of mechanical weathering Cycles of freezing and thawing can cause ice wedging, which can break rock into pieces The cycle of ice wedging starts when water seeps into cracks in aMechanical (Physical) Weathering It is a natural process of insitu disintegration of rocks into smaller fragments and particles through essentially physical processes without a change inTwo Types of Weathering 1 Mechanical weathering is the breaking down of rock without any change in the chemical composition of the rock – Sometimes called "physical" weathering – Rock is torn apart by physical force, rather than by chemical breakdown – Smaller pieces do not move to a new location, but remain next to one another until erosion carries them away




Mr Gruszka S Earth Science Giftionary Day 048 Giftionary Physical Weathering




Reading Weathering Geology
Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rocks into sediments through physical means Unlike chemical weathering, mechanical weathering does not alter the chemical composition of the rock One way that trees mechanically weather rocks is through their root systems These roots serve as an anchor to absorb water But at the same time, they pry away at soil and rocksWeathering describes the physical removal of sediments from one place to another, while erosion is the chemical breakdown that forms those sediments Weathering is when oxygen attacks the rock, while erosion is when water freezes in the cracks causing the Tamang sagot sa tanong Hering A type of weathering where there is physical wearingaway of rocks temperature The result of breaking down of rocksweatherings The process by which the rocks break into smaller pieceschemical wealtype of weathering where change in the composition of rockshappens5 An agent of weathering that can cause sand and dirt to be blown away6 An agent of weathering




Weathering Physical Chemical Biological Weathering



Erosion And Weathering
Mechanical – physical changes causes rocks to break down, for example, a change in temperature from day to night causes rock to expand and contract and break up (eg onion skin weathering)Over time, movements of the Earth and environment can break apart rock formations Pressure, warm temperatures, water, and ice are common causes of physical weatheringPhysical mechanical chemical breakdown smaller transportation settling May 17638 AM Weathering Two types of weathering 1 _____ (_____) 2 _____ Physical Mechanical Chemical May 17638 AM Physical Weathering Any process that causes a rock to crack or _____ into pieces _____ chemically changing the rock break WITHOUT May 17638 AM



Physical Weathering Processes Of Change




Activity 3 Time Lapsedirections Choose Any Of The Three Types Of Weathering Show How Rocksbreak Brainly Ph
Weathering is the process that changes solid rock into sediments With weathering, rock is disintegrated into smaller pieces Once these sediments are separated from the rocks, erosion is the process that moves the sediments away from it's original position The four forces of erosion are water, wind, glaciers, and gravityPhysical weathering is a term used in science that refers to the geological process of rocks breaking apart without changing their chemical composition What causes weathering to occur? All of these processes break rocks into smaller pieces without changing the physical composition of the rock How can we prevent chemical weathering?
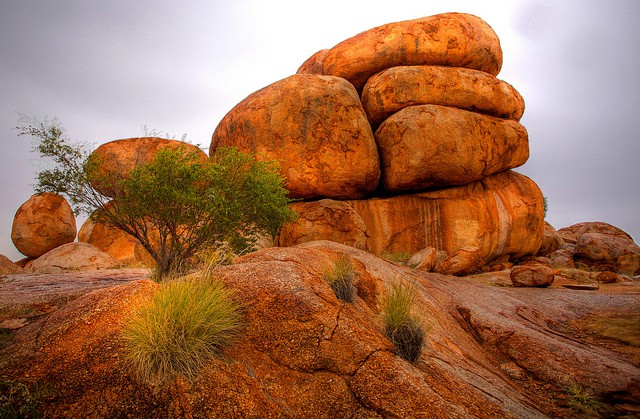




What Is Weathering And Different Types Of Weathering Earth Eclipse



Weathering Erosion 3 Rock Types
The mechanical and chemical processes that change objects on Earth's surface over time;Rocks can break down into smaller pieces by the interaction on them by plants and animals When a rock develops cracks small rock particles and soil are washed into such a crack by rain or wind If a seed should drop into such a crack, it can germinate and can grow to become a plantThe frozen water expands and causes the rocks to weaken and widens the cracks In the longrun, the bigger rocks are broken into smaller and smaller fragments Moving ice in glacial areas also washes away rock fragments and disintegrates them into smaller pieces as the rocks interact with the forces and pressure of the frozen materials




Physical Weathering Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




How Do Rocks Break Educational Resources K12 Learning Earth Science Science Lesson Plans Activities Experiments Homeschool Help
Over time, natural forces break rocks into smaller and smaller pieces If you have ever seen a concrete sidewalk or driveway that has been cracked by tree roots, you have seen this processIf a rock is heated and cooled many times, cracks form and pieces of rock fall away This type of physical weathering happens a lot in deserts, because it is very hot during the day but very coldWeathering breaks rocks into smaller pieces Think about the tiniest rock you have ever found How did it get so small?



Erosion And Weathering




How Does Weathering Erosion Deposition Act In A
Power washing cement or asphalt surfaces, and weeding regularly, will prevent the breaking down of such surfaces from the decomposition induced by acids released by lichens or mossesOver time, movements of the earth and environment can break apart rock formations, causing physical weathering Physical weathering is affected by a number of things in the environment including soil and minerals, animals, pressure, changes in temperature, water and ice After a rock has weathered, erosion occurs, transporting bits and pieces awayPhysical weathering contains several processes thermal expansion, frost wedging, exfoliation, abrasion, and salt crystal growth Each of these results in the breakdown of rock into smaller sediments In this experiment we will demonstrate the breakdown via abrasion Rocks are constantly ground down by the effects of water, wind and ice




Learning Geology Weathering And Erosion




Weathering Understanding Global Change
Mechanical weathering is the physical breakdown of rock into smaller pieces Chemical weathering is the breakdown of rock by chemical processes Ice can also cause mechanical weathering when water gets in cracks in rocks, and then freezes and expandsPhysical Weathering Physical factors such as freezing and thawing, temperature, rain, winds, waves, water pressure, and others can cause rocks to break up into tiny pieces Specific types of physical weathering occur in specific places Here are a few examples Physical (mechanical) weathering changes the size and/or shape of the rock It does not change the rock's chemical composition Physical weathering is caused by the effects of changing temperature on rocks, causing the rock to break apart




Chemical Weathering An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Pin On Rocks
This article throws light upon the two types of weathering of rocks The types are 1 Chemical Weathering 2 Physical or Mechanical Weathering Type # 1 Chemical Weathering Chemical weathering is the basic process by which denudation proceeds It is the extremely slow and gradual decomposition of rocks due to exposure to air and waterPhysical Weathering Physical or mechanical weathering is the disintegration of rock into smaller pieces Chemical Weathering Water Erosion Wind Erosion Gravity What are the 5 main causes of physical weathering?Physical Weathering Physical weathering is caused by the effects of changing temperature on rocks, causing the rock to break apart The process is sometimes assisted by water Freezethaw occurs when water continually seeps into cracks, freezes and expands, eventually breaking the rock




Examples Of Physical Weathering



Q Tbn And9gcrkqovobrv4jovomer39t8lzy8o58cx F5ibdcv0qrxew6sx9j2 Usqp Cau
Mechanical Weathering Mechanical weathering involves all processes that collectively break rocks into smaller pieces (see examples in Figures 92 to 910)Mechanical weathering includes all forms of mass wasting—a general name for processes by which soil and rock move downslope under the force of gravityMass wasting, a form of mechanical weathering, includes sudden events such as rockIn addition to physical weathering, rocks can be broken down by chemical means Chemical weathering happens when rocks break down because of chemical reactions Water, acids, and air are all agents of chemical weathering They react with the chemicals in the rock The reactions can break the bonds in the minerals that make up the rock When the bonds in the minerals areAll rocks on the Earth's surface weather though some weather faster than others Three different forces work together to break up rocks into smaller pieces 1 Physical weathering cycles of hot and cold temperatures make rocks expand and contract, and rain may freeze and expand in cracks in the rock These processes eventually lead to rocks



Weathering And Erosion Earth Processes Onegeology Kids Extra Onegeology




Biological Weathering Examples And Definition Science Trends
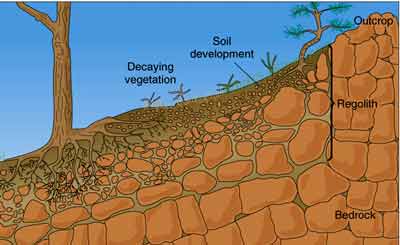
The weathering of rocks on the Earth's surface results in the formation of soil Soil is formed when rocks are continuously broken down by weathering As rocks weather, they break into smaller pieces These pieces are broken down into even smaller pieces to form soilWeatheringThe breakdown of rocks and minerals into pieces or dissolveCrumbling or adjustment of rock in its characteristic or unique situation at or close to the Earth's surface through physical, synthetic, and natural cycles actuated or altered by wind, water, and environmentThe more exposed the rock is to weathering, the more it becomes very vulnerable to breakingWeathering is the combination of processes that breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals, eventually transforming into sedimentOn the other hand, disintegration or alteration of the rock surface in its natural or original position through physical, chemical and biological processes induced or modified by wind, water and climate



1




Weathering Physical Mechanical Weathering
Weathering and Soil Andrew Brown, Ecoscene/CORBIS Soil is a natural resource that must be monitored, managed, and protected SECTION 1 Weathering Main Idea Weathering processes weaken and break apart rock material into smaller pieces SECTION 2 The Nature of Soil Main Idea Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, decayed organic matter, mineral*Breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by critters, plants, etc Results of Mechanical Weathering Talus Cones (From ice wedging mostly) Boulder fields (From ice wedging mostly) Jointing Cracks in the rock from ice wedging and sheeting Chemical Weathering Rocks are decomposed and the internal structure of the minerals isWhat is physical weathering?




3 1 Study Guide




Weathering National Geographic Society




Weathering And Erosion




Soils Weathering




Reading Mechanical Weathering Geology




Mechanical Weathering Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation



Physical And Chemical Weathering Of Rocks Geography Realm



Title




Epic Weathering And Erosion Review For 6 Th




Chemical Weathering An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Weathering And Erosion Earth Processes Onegeology Kids Extra Onegeology




Weathering The Process Of Breaking Down Of Rocks Into Smaller And Smaller Pieces Of Rock These Small Pieces Are Known As Sediment Sediment Breaks Down Ppt Download



Types Of Weathering Storyboard By Oliversmith



Physical And Chemical Weathering Of Rocks Geography Realm




Frost Wedging Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



1
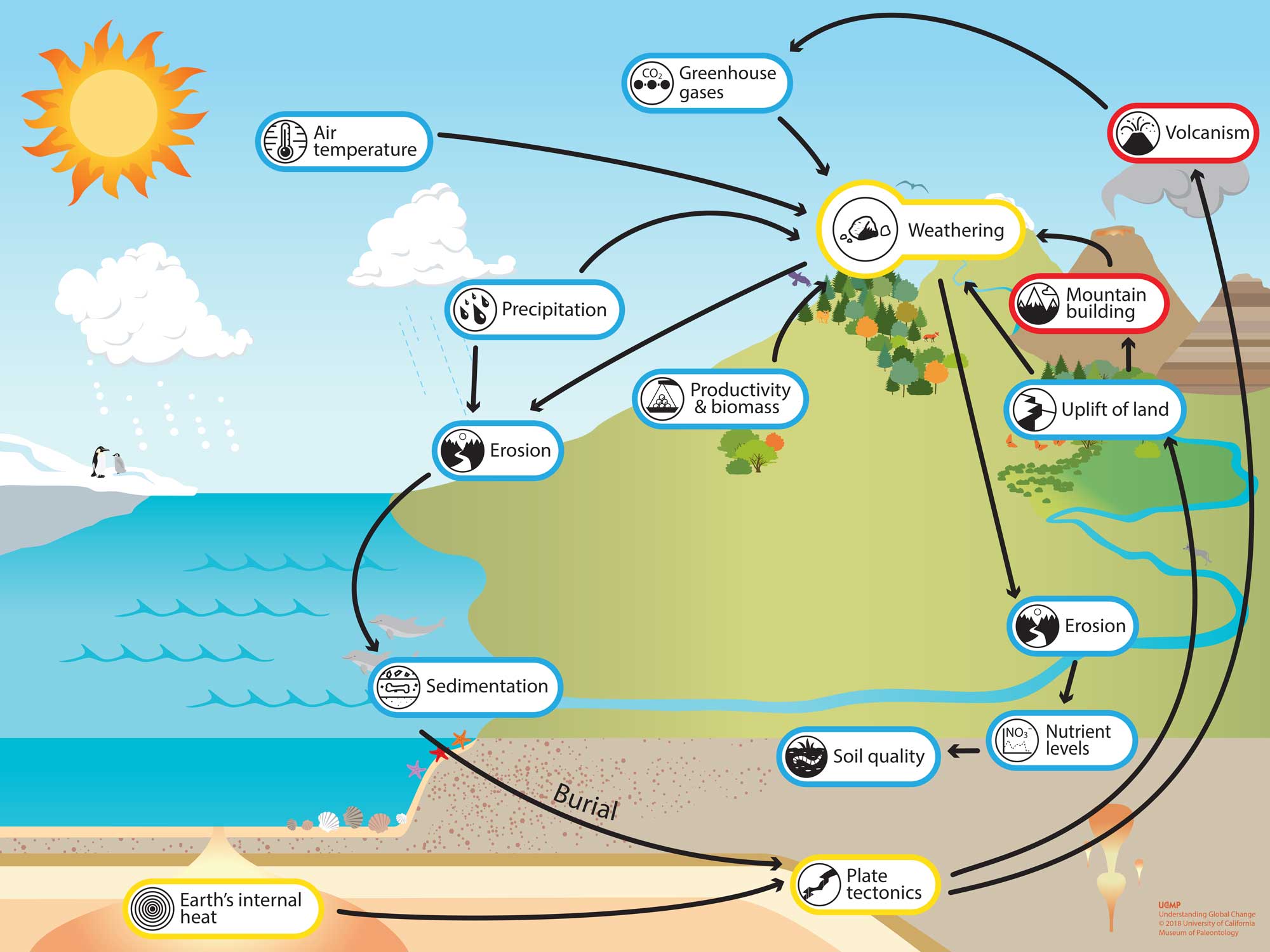



Weathering Understanding Global Change




Weathering The Process By Which Rock Is Broken Down Into Smaller Pieces May Be Physical Or Mechanical They Mean The Same Thing May Be Chemical May Be Ppt Download



Exogenic Processes




Geology Cafe Com



Geography4kids Com Biosphere Weathering



5 1 Mechanical Weathering Physical Geology




Aim What Causes Weathering And Erosion Weathering Is The Physical And Chemical Breakdown Of Rocks Into Smaller Pieces Called Sediment Due To Air Ppt Download




Learning Geology Weathering And Erosion




Lesson 1 Weathering Weathering Acts Mechanically And Chemically To Break Down Rocks Through The Action Of Earth Processes Such As Freezing And Thawing Ppt Video Online Download




Weathering And Erosion Questions Flashcards Quizlet




What Is Weathering Soils Matter Get The Scoop
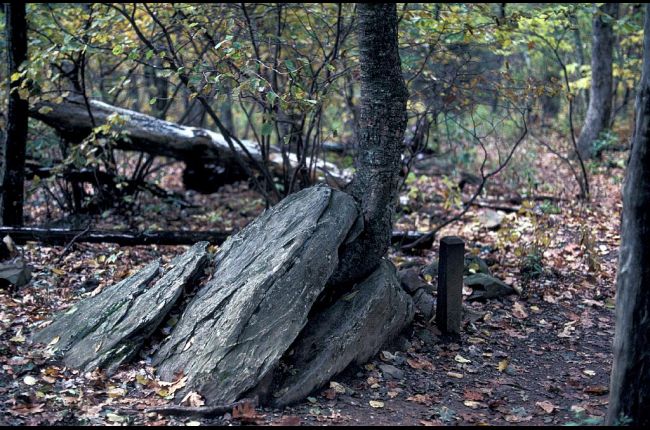




What Is Physical Weathering American Geosciences Institute



Weathering Of Rocks River Sea Oceans Temperature Important Salt System Oxygen



Q Tbn And9gcs01sfty12zfi7r9r0cel0gdvdlgyehrk4hkq Xrergqrf1yhwp Usqp Cau




Stem Engine Earth Science Exogenic Processes Facebook




Four Types Of Physical Weathering




Four Types Of Physical Weathering



Geography4kids Com Biosphere Weathering
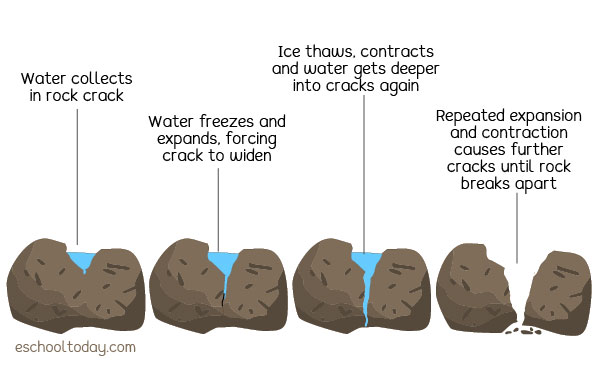



What Is Physical Weathering Of Rocks Eschooltoday




Physical Weathering Geolearning Department Of Earth Sciences




Weathering Is An Important Process That Helped Shape The Earth S Surface It Is The Breaking Down Of Brainly Ph




Mechanical And Chemical Weathering Flashcards Quizlet




Reading Weathering Geology



Weathering Pgce Geography Classroom



Four Types Of Physical Weathering




Weathering Wikiversity



Weathering Erosion Deposition Mrs Allen S Earth Science Pages




Examples Of Mechanical Weathering Science Project Education Com




What Are The Two Types Of Weathering




Reading Mechanical Weathering Geology



Geol342 Sedimentation And Stratigraphy




Weathering Ppt Download
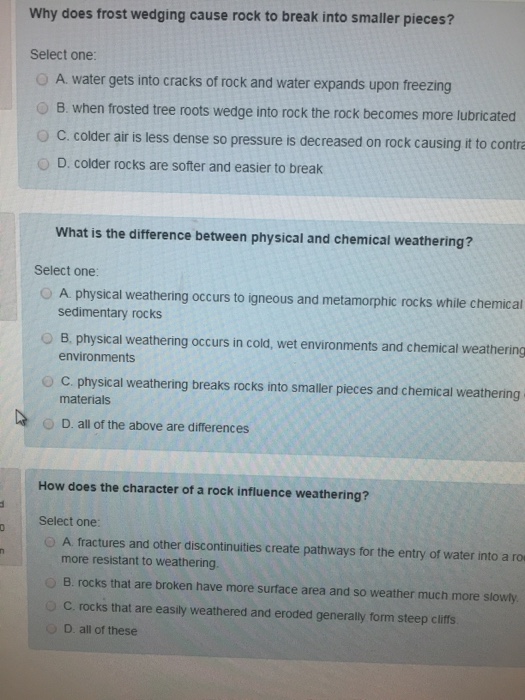



Why Does Frost Wedging Cause Rock To Break Into Chegg Com




Physical Weathering Day One Physical Weathering The Process



Weathering Definition And Types Physical And Chemical Weathering




Weathering National Geographic Society




What Is Weathering And How Does It Shape Landforms Eschooltoday




Pdf Geomorphic Weathering




Weathering And Erosion



Http Www Chittenangoschools Org Tfiles Folder3345 Weathering erosion deposition review notes Pdf



The Breakdown Of Rock Into Smaller And Smaller Pieces Ppt Video Online Download



11 3 Weathering Earth 002 Earth Sci Lab Haddad E Winter 21 Section




Ppt Weathering Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Lesson 1 Weathering Weathering Acts Mechanically And Chemically To Break Down Rocks Through The Action Of Earth Processes Such As Freezing And Thawing Ppt Video Online Download




Weathering Is The Breakdown Of Rocks Into Smaller Particles Called Weathering Is When Rocks Are Brainly Com




Weathering Wikipedia




Weathering Physical Weathering Process By Which Rocks And




Aim What Causes Weathering And Erosion Weathering Is The Physical And Chemical Breakdown Of Rocks Into Smaller Pieces Called Sediment Due To Air Ppt Download



Geography 101 Online




Weathering Erosion Deposition 8th Grade Science



Frost Weathering Wikipedia
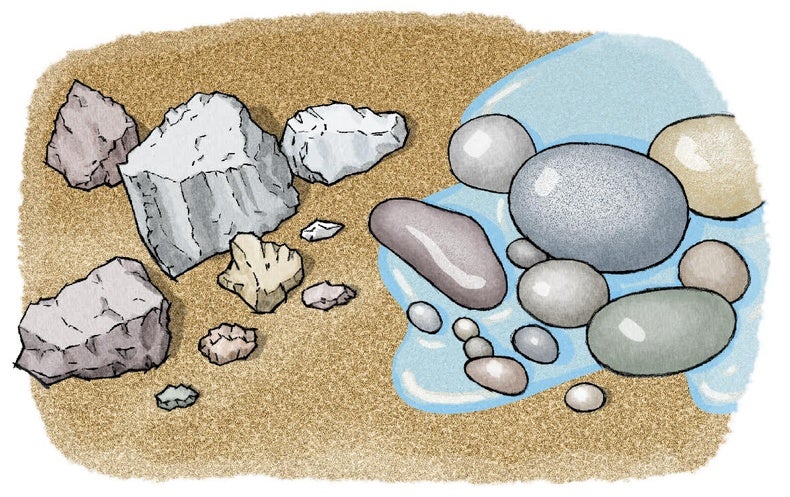




Weathering Rocks Scientific American
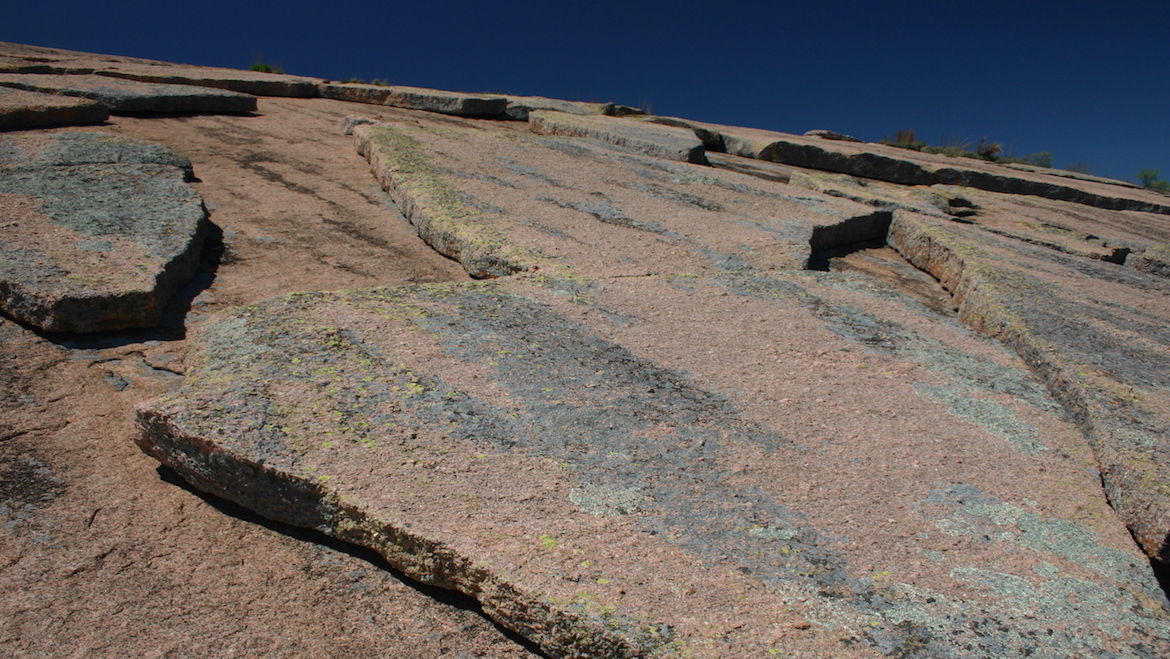




8 1 Mechanical Weathering Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition




Weathering How Did This Happen To The Rock
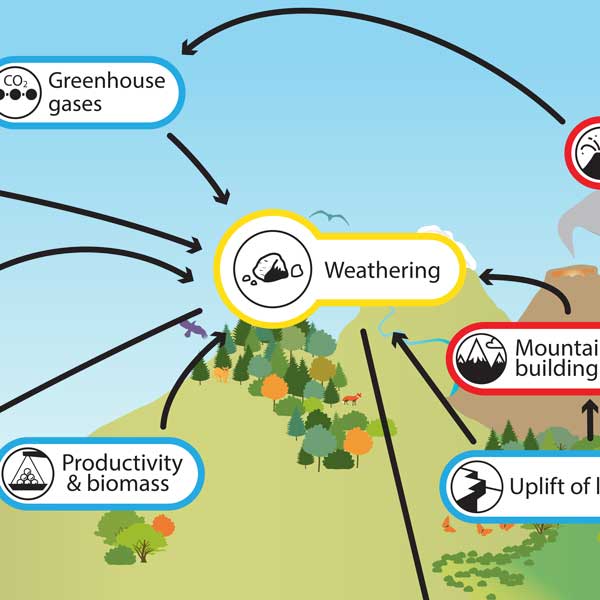



Weathering Understanding Global Change




Weathering Erosion And Soils
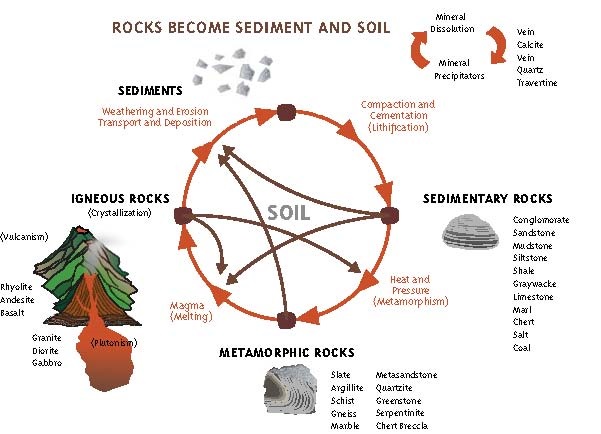



Soil Weathering Processes Soils 4 Teachers



The Learning Zone Rock Cycle




Weathering It Types




Weathering Lesson For Kids Definition Facts Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
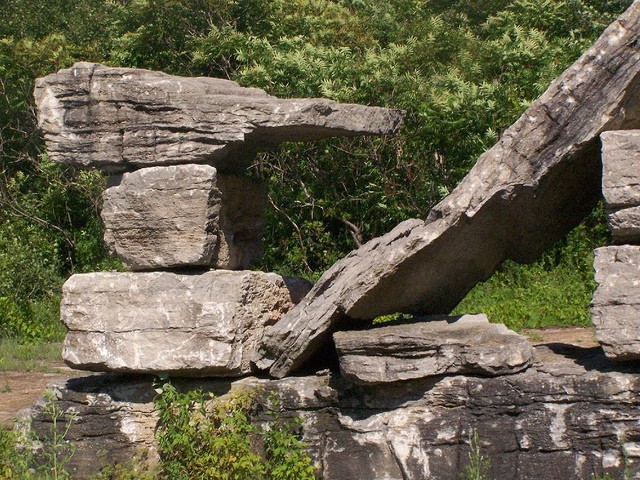




Physical Weathering Definition Processes And Types Earth Eclipse
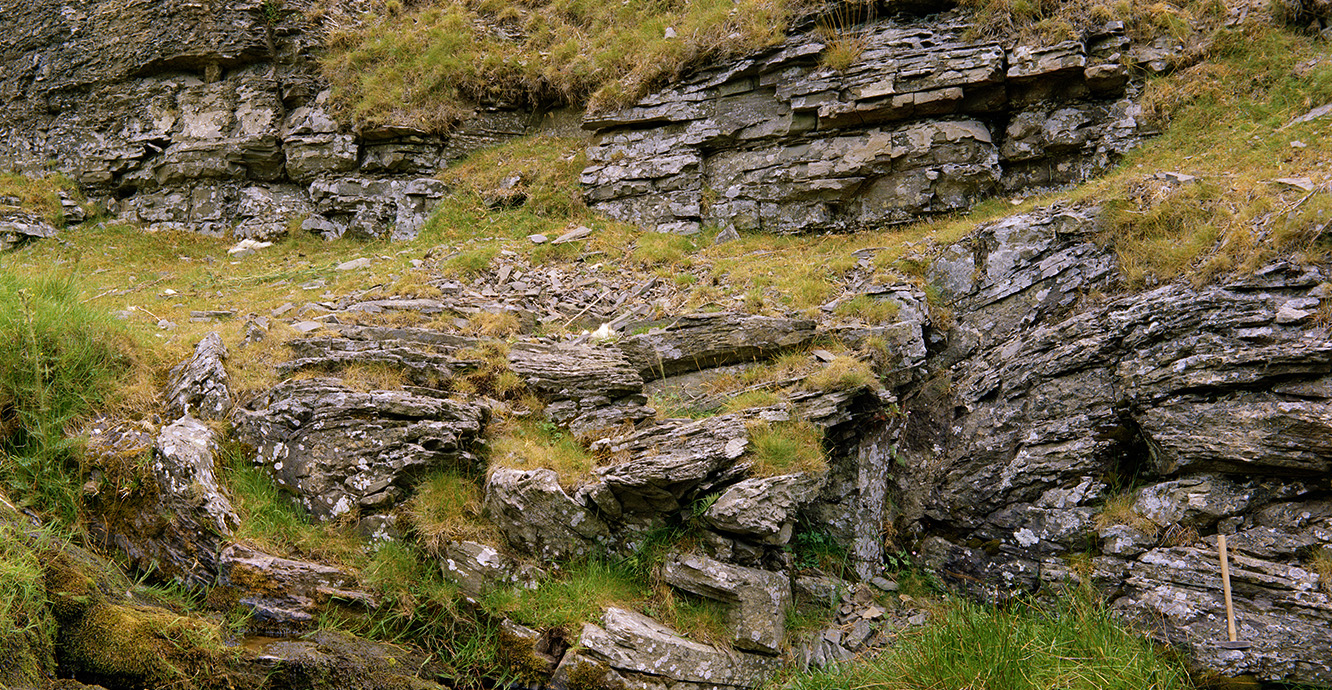




Weathering British Geological Survey




Weathering Erosion




High School Earth Science Weathering Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Weathering And Soil Rocks And Weathering Uniformitarianism The



Physical Weathering Processes Of Change


